Publications > Article
Evaluating Nature-Based Solutions for Water Management in Peri-Urban Areas
The term nature-based solutions (NBS) has gained traction in recent years and has been applied in many settings. There are few comprehensive assessment frameworks available that can guide NBS planning and implementation while at the same time capturing the short- and long-term impacts and benefits of the NBS. Here a recently presented framework, which builds on the theory of change and was developed to assess NBS at different phases of the project cycle, was applied to seven diverse case studies.
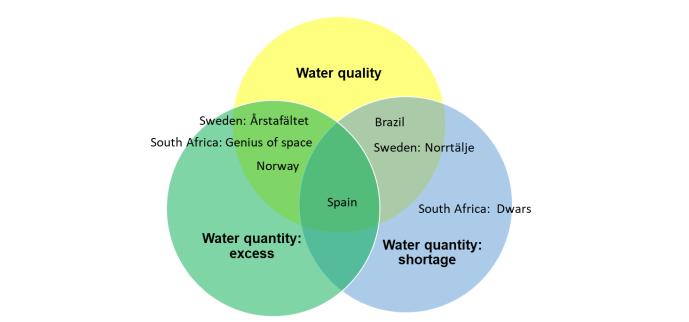
The case studies addressed water quality and quantity issues in periurban areas across the global north and south. Framework indicators covering the sustainability dimensions (environmental, social and economic) were assessed at three stages of the framework: context, process and results. The work sought to investigate the following research objectives:
- (1) Can this framework be robust and yet flexible enough to be applied across a diverse selection of NBS projects that are at different phases of the project cycle and address different kinds of water challenges within varied ecological, social and economic contexts?
- (2) Is it possible to draw generalisations from a comparative analysis of the application of the framework to the case studies?
Results showed that the framework was able to be applied to the case studies; however, their diversity showed that NBS projects designed in one context, for a specific purpose in a specific location, can not necessarily be transferred easily to another location.
There were several process-based indicators that were universally significant for the case studies, including expertise, skills and knowledge of the involved actors, roles and responsibilities of involved actors and political support.The resultbased indicators were case study-specific when environmental indicators were case study-specific, and important social indicators were environmental identity and recreational values. Overall, the use of the framework benefits the recognition of the implementation’s advances, such as the change in context, the processes in place and the results obtained.